Saturday, July 3, 2010
WEEK 13 ( 28 JUNE- 2 JULY)
Tuesday, June 29, 2010
WEEK 12 (21-25 JUNE)
Monday, June 28, 2010
WEEK 11 (14-18 JUNE)
Monday, June 21, 2010
WEEK 10 (7-11 JUNE)
Beginning of this week, my colleagues and I had a meeting with our boss. We discussed about all our task that have been done for the past 2 months. In the meeting, I have been briefed about call routing strategies and virtual contact center. Besides that, I was also given new tasks for the week.
Nowadays, someone in England can make a phone call to Australia, or that someone in United States can read web pages that are on a computer in Canada. A large network is affected by many factors which are often hard to predict. There can be busy and quiet periods through the day. For example, if a television program has a phone-in vote, there can be a sudden overload at one point in the network. This is when routing calls comes in handy. These routing schemes work by searching out the spare capacity in the network so as to route calls away from parts of the network that are broken or full and into parts that are underloaded.
- last agent
- round robin
- lowest total talk time
- fewest received calls

Vendor Approaches
Blended Call Centers
Premise-Based Contact Center
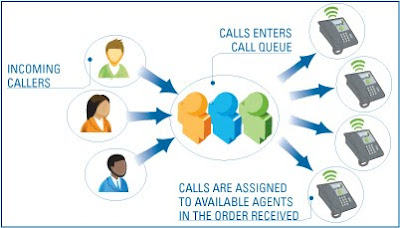
- Call Queue is to offer customer the best waiting time possible.
- Call Distribution Strategy : supervise talk time (average 3 min) and supervise the etiquette of agents.
Friday, June 4, 2010
WEEK 9 (31 MAY- 4 JUNE)
WEEK 8 (24-28 MAY)
- Collect traffic data
- Determine the Average Busy Hour
- Choose a target Grade of Service
- Use Erlang B
Besides that, there are more functions for Erlang B in excel such as ErlbNsrvFromBlockage and ErlbTrafFromBlockage.
Example of Excel Function for Erlang C:
Saturday, May 29, 2010
WEEK 7 (17-21 MAY)
Suppliers that I manage to find are as listed below:
- The Festvox Project
- Cepstral
- Acapela
- Power Text to Speech Reader 2.31
- Sayvoice Text to Speech Reader
- Word Talk
- ACE-HIGH
- Sayz Me
- NextUp Talker
- Loquendo
- Nobel Systems
- Aspect
- Cisco
- Computer Talk.Tech
- Upstream Works
- Zeacom
- Interactive Intelligents
- LumenVox
- TouchStar
- Siebel
- Cincom
- Contactual
- Envox Worldwide
- LivePerson
- Smoothstone
- TeleTech
- UCN
- Five9
- Packet8
WEEK 6 (10-14 MAY)
Step 2: Select an Audio Output Device.
Step 4: Configure Text-to-Speech Options.
- Transform the PCM digital audio into a better acoustic representation.
- Apply a "grammar" so the speech recognizer knows what phonemes to expect. A grammar could be anything from a context-free grammar to full-blown Language.
- Figure out which phonemes are spoken.
- Convert the phonemes into words.
WEEK 5 (3-7 MAY)
This week task was based on R&D. The topic given to me was Call Queuing. Call Queuing is a method of handling calls until they can be answered by an agent. Call Queuing is a sophisticated queuing system that allows you to accept more calls into your telephone system than you have extensions or employees capable of answering them.
Sunday, May 9, 2010
WEEK 4 (26-30 APRIL)
- Create an user extension in file editor. (Created user extension will appear in ring groups. The user extension is created by typing coding into the config files.)
- Edit Ring Groups.
- Select strategy either Ring all or Ring in order. (Ring all is Find me which rings simultaneously. Ring in order is Follow me which rings sequentially.)
- User extensions in available channels are sent to ring group members.
- Test Calls ( 3 different subscribers receive calls simultaneously and sequentially from one caller)

The next practical task was 3-party voice conferencing which test call from subscriber 1 to subscriber 2 and subscriber 3 able to listento the conversation.
The basic concept of audio conferencing uses two or more speakerphones and several dial up numbers. With most services, the user would set up a meeting for a specific time and there will be either local or toll free numbers available for each person to call in on. They would in turn enter the required information to gain access to the meeting that you have been invited to attend. Then everyone is either on a single handset or at a table surrounding a speakerphone of some type. This is accomplished by the use of a pin number entry system and then the only people that will have access to the meeting are those that have provided with a pin number. The user can change the pin number for each meeting, providing greater levels of security.
Below are the steps for 3-party voice conferencing:
- Create an user extension in file editor. (Created user extension will appear in ring groups. The user extension is created by typing coding into the config files.)
- Configure Conference Bridge Extensions. (New extension is created by clicking new in conference bridges)
- Edit conference room options.
- Test Calls. (3 different subscribers able to do audio conferencing)
 Audio Conferencing
Audio Conferencing
After carrying on all the practical task, I documented all the testing and findings. The test plan document was done to be sent to the main branch.
Saturday, May 8, 2010
WEEK 3 (19-23 APRIL)

How an IP phone works

Configuration in Asterisk server
End of the week, I was asked to do some research. I was given 3 research topics. First topic was IVR customiztion. IVR stands for Interactive Voice Response. It is the technology that we use everyday when we call a bank or a hospital or any large business. It is the voice activated prompts that brings us to the correct person or gives us the answer we want. IVR automates inbound call routing and fosters self-service.The whole process of placing an order by the caller, and checking the status with the help of the order number can be automated with the customized IVR flow. During wait time or hold time, messages about other products and promotional offers can also be played allowing you to capitalize on cross-selling and up-selling opportunities. For example a customer may ask for a "Meal for two" instead of two individual pizzas after listening to the offer while he was in the queue.

IVR application
The second topic was Find Me/Follow Me. Find me and follow me are two call forwading services that are commonly used in conjunction with each other. Find me service allows the user to receive calls at any location. Whereas follow me service allows the user to be reached at any of several phone numbers. Find me / follow me numbers use VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) technology to route all of the incoming calls to one single telephone number. These numbers let the users consolidate their communication devices.

Find Me/Follow Me
The last topic for the week was 3-party voice conferencing. Voice conferencing is one of the most critical elements of group communication. Excellent voice quality is essential for both voice-only calls and visual communication environments, ensuring that everyone can clearly hear and be heard to improve productivity and deliver a seamless, natural communications experience.
Below are the steps to setup a third-party conferencing service to be the main audio conference solution:
1. As the host, enter the meeting room.
2. Select the Meeting menu.
3. Select Set phone conference options. The Phone Conference Options appears.
4. Select Other.
5. Enter the conference number.
6. Enter the participant code.
7. Enter the Moderator code.
8. Click OK.

Audio Conferencing
Sunday, April 18, 2010
WEEK 2 (12-16 APRIL)
This week was kinda exciting. Beginning of the week, I did some research on Session Initiation Protocol (SIP). SIP is a signaling protocol used for establishing sessions in an IP network. The protocol can be used for creating, modifying and terminating two-party (unicast) or multi-party (multicast) sessions consisting of one or several media streams. SIP responses are the codecs used by SIP for communication. The codecs that I focused was g729, g726 and g711.

The next day, I was exposed to Welltech 6500 and Wellrec 5600. Welltech is the IP PBX system to operate on a variety of VoIP applications. The Welltech WellCIP 6500 series SIP Telephony server is the best choice to convergence VoIP network which convert the requirements from enterprise to service provider. Wellrec 5600 is a VoIP recoder for Welltech SIP network architecture.
My last task for the week was building a custom Interactive Voice Response (IVR). IVR is a technology that automates interactions with telephone calls. I downloaded Zoiper softphone from internet and configured the settings with my user extension. Then, I connected the IP phone and made phone calls from the IP phone to the softphone and vice versa.
Saturday, April 17, 2010
WEEK 1 (6 - 9 APRIL)
After that, I was assigned with my first task. My first task was to create an operator service (Virtual PBX). PBX used to calls answered with a custom business greeting, offer an audio scroll-through of your employee directory, provide a connection directly to a specific person or department, play music while the system is in hold, and even take voice mail for emloyees. Firstly, I google AT&T TTS and IBM. TTS is the creation of audible speech from computer readable text. Then, I typed out a speech text and clicked download. Next, I opened the downloaded wavefile in wavepad and edited the voice. Finally, the edited voice was uploaded in uniceed demo account under UC settings in multilevel Virtual PBX.
Besides that, I also learned about Web ticketing and online chat system this week. This was done by creating an account in supportuniceed/staffs and browsing the system. Other than that, I learned about Asterisk and AsteriskNow. Asterisk is an open source telephony project. It turns an ordinary computer into a feature-rich voice communications server. Asterisk includes all the building blocks needed to create a PBX system, an IVR system. AsteriskNow creates custom telephony solutions by automatically installing the "plumbing".

Saturday, April 10, 2010
FIRST DAY OF INDUSTRIAL TRAINING (5 APRIL)

Services that UNICEED offers are:-
-Voice-to-Email/ Fax-to-Email
-SMS Messaging
-Divert calls
-Virtual PBX
-Interactive Voice Response
-Find Me/ Follow Me
-Multi-party Video Conferencing
-SMS Notifications
-Fax Forwading
My working hours is from 10am to 7pm. Since it's my first day, I left my house early and arrived at the Gardens South Tower lobby at 9.30am. At the lobby, I met 3 of my friends who also got the same placement. After reaching the office, Mr. Jeffrey, CEO, gave us a brief introduction about the company and the services. Since it's a new branch, the office is very small and not many staffs. The main branch is at Cyberjaya.
 Our Workstation for 3 months
Our Workstation for 3 monthsWelcome to ABC company!
For sales, press 1
For customer service, press 2
For technical, press 3

























.jpg)
.jpg)


.jpg)